Overview
vk hmm [options] --A=<parent_1> --B=<parent_2> <vcf>
The vk hmm uses a hidden-markov-model to call near-isogenic lines (NILs) or recombinant-inbred lines (RILs). The hmm command is designed for use with low-coverage sequence data from RIL or NIL populations. The HMM is designed to detect parental haplotypes while ignoring sequencing errors. However, it is not as sophisticated as alternatives such as such as Impute2 or Beagle which can also be used to perform this type of analysis, although you may need to modify your VCF or generate input files.
--A=<parent_1>- The first parent. Can also beREF.--B=<parent_2>- The second parent. Can also beALT.
To use the vk hmm command, you'll need a VCF with these requirements:
- The parents must be represented within the VCF or their genotypes must be represented as REF (all 0/0) or ALT (all 1/1) calls.
We have had success using the vk hmm command whole genome sequencing strains of C. elegans at very low depth (~1.5x). Genotyping arrays can also be used.
The vk hmm command iterates through the VCF, assembles an array of genotypes, and uses an hmm to assign parental haplotypes.
Options
--vcf-out- Outputs a VCF, assigning genotypes based on parental haplotypes called by the hmm. AGT_ORIGformat field is added to retain the original genotype call.--endfill- When outputting genomic regions, if a parental genotype is assigned at the very beginning or end of a chromosome use 1 or the length of the chromosome, respectively. The endfill option is recommended for near-isogenic lines, and not for recombinant inbred lines.--infill- Assume genotypes switch at the end position of the previous block + 1 rather than the next observed genotype. This removes gaps and is useful for aesthetics, but should probably not be used for analysis.--state- Probability of ref/alt state, accounting for errors. For example, if --state=0.97, the probability the calls are reference is 97% and 3% of calls will be alt (attributable to errors).--transition- Probability of transition occuring. We set this very low by default because the state probability accounts for some level of error.
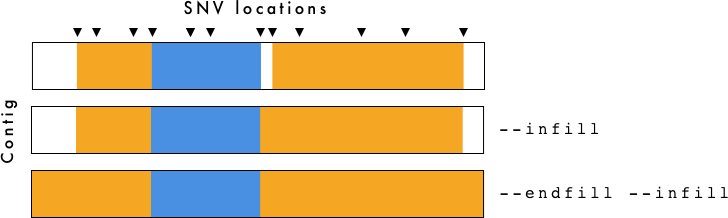 Effect of using
Effect of using --infill and --endfill options - Orange and blue parental haplotypes can extend to the beginning or end of chromosomes using the --endfill option whereas regions between adjacent SNVs where haplotypes switch can be filled in with the next haplotype.
Recommended Filters
vcf hmm can take stdout as input. When working with low-coverage whole-genome sequence data, we recommend applying filters to remove problematic sites. Specficially, the DV/DP ratio can be used to remove problematic alt sites using the command below:
bcftools view <vcf> |\
bcftools filter --set-GTs . --exclude '((FMT/DV)/(FMT/DP) < 0.75 && FMT/GT == "1/1")' |\
vk hmm --A=<parent_1> --B=<parent_2> --ref=<ref_sample> -
Plotting Results
This R script can be used to plot. An example is below.
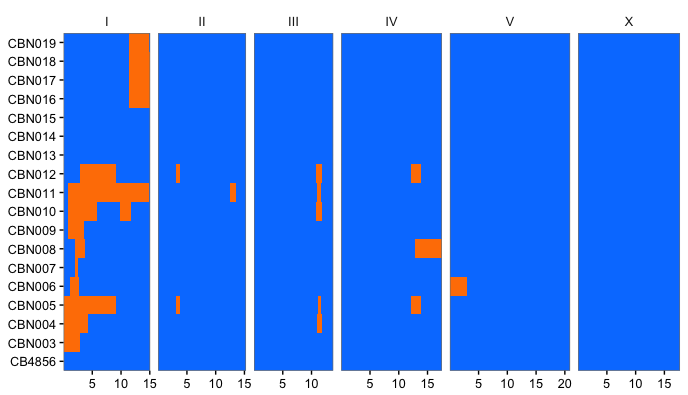
Output
TSV
If you do not use the --vcf-out flag, out put will be a tsv:
| chrom | start | end | sample | gt | gt_name | supporting_sites | sites | DP | switches | rle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | 77451 | 7920553 | ECA651 | 1 | N2 | 1259 | 1265 | 1.06593 | 12 | B59A1A360A1A288A1A83A1A302A1A45A1A122 |
| IV | 7930759 | 9519760 | ECA651 | 2 | CB4856 | 78 | 83 | 1.14103 | 10 | A32A1A20A1A3A1A4A1A14A1A5 |
| IV | 9542273 | 17491919 | ECA651 | 1 | N2 | 1134 | 1139 | 1.12875 | 10 | B333A1A38A1A335A1A79A1A336A1A13 |
The following columns will be listed
chrom- Chromosomestart- The start of the haplotype call.end- The end of the haplotype callsample- The samplegt- A numeric representation of the parental haplotype called. Corresponds with thegt_namecolumn.gt_name- The parental haplotype calledsupporting_sites- The number of genotypes supporting the parental haplotype call.sites- The total number of genotypes found within the region (does not include missing).DP- The average depth of genotype calls in the region.switches- The number of switches that occur between parental genotypes within a haplotype.rle- The run-length-encoding of the genotypes called.B3A1B8represents 3 B-parent calls, 1 A-parent call, and 8 B-parent calls.
VCF
If you use the --vcf-out flag, the output will be a VCF. The FORMAT/GT field will be flipped for the appropriate genotype call. Additionally, a FORMAT/GT_ORIG field will be added indicating the original genotype.